
Polyester, nylon , spandex, polypropylene… I can’t tell them apart
In the past, there was no online shopping and no big shopping malls. There were only noisy markets, crowded crowds, and shopping malls on both sides of the road. While shouting, she was picking this thing and that thing… The woman picked up the crisp and stylish little suit at hand and turned to the door, “Boss, is this fabric of yours really good?” “No, it’s nylon.”
The story is to be continued, here comes the question: What are Dacron, nylon, polyester, spandex, polypropylene and acrylic?
They are all textile fibers.
Fiber is a natural or synthetic filament-like substance, such as cotton, wool, silk, man-made fiber, synthetic fiber, etc., and textile fiber It refers to the fibers used to weave cloth.
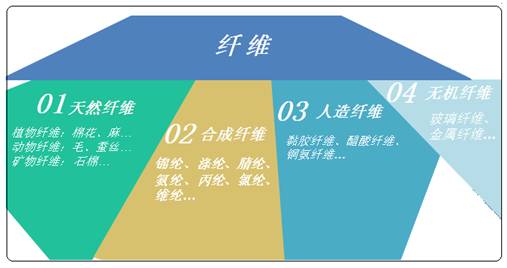
Natural fiber textile fabrics are hygroscopic, breathable, elastic and comfortable in texture, and have been favored by consumers since ancient times. Driven by chemistry and material science, synthetic fibers have already penetrated into thousands of households. Today we will learn about the connections and differences between their “fiber families”.
“Lun Family” Contact

First of all, this The name is very elegant, isn’t it? “Lun” means “thread”. You may think of “a child with unkempt hair learns fishing”
scene, here, it should refer to the long chain of polymers formed by the polymerization of monomers. Members of the fiber family are all synthetic linear fiber-forming polymers with suitable molecular weight and soluble (or fusible) properties, which are produced through spinning and post-processing. In addition to the general superior properties of chemical fibers, such as high strength, light weight, easy washing and quick drying, good elasticity, and resistance to mildew, different types of synthetic fibers also have their own unique properties.
The difference between “Lun family”

Internal: different monomers
The structural unit of polyester is ethylene terephthalate, with the molecular formula [- OC-Ph-COOCH2CH2O-]n, so it is also called polyester fiber (PET). The relative molecular weight is generally around 1.8~2.5w.
Nylon is often referred to as nylon, and its scientific name is amide fiber. The structural units are of course connected through amide bonds [-NHCO-] Aliphatic polyamide.
Spandex is the abbreviation of polyurethane fiber (PU) and is an elastic fiber. There are two varieties of spandex, one is a mosaic copolymer of aromatic diisocyanate and hydroxyl polyester segments (referred to as polyester spandex), and the other is a mosaic copolymer with hydroxyl polyether segments (referred to as polyether spandex) .
Polypropylene, which is polypropylene (PP) fiber, molecular formula [-CH2CH(CH3)-].
Acrylic fiber is a synthetic fiber made of polyacrylonitrile or an acrylonitrile copolymer with an acrylonitrile content greater than 85% (mass percentage) . Pure acrylic fiber has poor wearing properties (basic performance and comfort performance). By adding the second and third monomers, its elasticity, feel, dyeability and other properties can be improved. Commonly used second monomers are non-ionic monomers, such as methyl acrylate, methyl methacrylate, etc., and the third monomer is ionic monomers such as sodium propylene sulfonate and 2-methylene-1,4- Succinic acid, etc.
Vinylon Also called vinylon, it is polyvinyl formal fiber. It mainly has a six-membered ring structure and can also be polymerized into five-membered fibers. Ring, known as “synthetic cotton”.
Polyvinyl chloride, that is, polyvinyl chloride fiber, molecular formula [―CH2-CHCl―]n, is the largest variety of plastics in the world. One of the earliest synthetic fibers in the world.
External appearance: different performance
Polyester : Stiff and wrinkle-free, good shape retention, wear-resistant, dimensionally stable, easy to wash and quick-drying. Filament is often used as low-elastic yarn to make various textiles; short fiber can be blended with cotton, wool, linen, etc., and is used industrially as tire cord, fishing nets, ropes, filter cloth, insulating materials, etc. Polyester is currently the most widely used chemical fiber.
Nylon: The fabric is light, has good elasticity, very good wear resistance, and poor air permeability. Filament is mostly used in knitting and silk industry; short fiber is mostly used in…Wool or wool-type chemical fiber blends. Industrially used as cords and fishing nets, carpets, ropes, conveyor belts, screens, etc.
Spandex: The highest elasticity, high elongation, soft and wrinkle-free feel, good wearability, often used as tight-fitting products, but No coloring, lowest strength. Spandex is a highly elastic fiber necessary for high-performance clothing that pursues dynamics and convenience. It is widely used in textile and medical fields such as underwear, casual wear, sportswear, socks, pantyhose, and bandages.
Polypropylene: The lightest texture, good warmth retention, wear-resistant, durable, and non-pilling. PP is an old friend of our original article. You must know that it is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic that often transforms into a water glass. You can knit socks, mosquito net cloth, quilt batting, thermal padding, diapers, etc. Industrially used as carpets, fishing nets, canvas, hoses, and medically used as sanitary products instead of cotton gauze.
Acrylic fiber: soft, bulky, easy to dye, brightly colored, light-resistant, antibacterial, fur-like, known as artificial wool . It can be spun purely or blended with natural fibers. Its textiles are made into a variety of wool, wool, blankets, sportswear, artificial fur, plush, bulked yarn, hoses, umbrella cloth, etc., and are widely used in clothing, decoration, industry and other fields.
Vinyllon: It has the best hygroscopicity, its performance is close to cotton, its wear resistance and strength are better than cotton, and it is mostly used for blending with cotton It is used to make knitted fabrics such as outerwear, cotton sweaters, sweatshirts, etc. It can also be used in canvas, fishing nets, surgical sutures, bicycle tire cords, filter materials, etc.
Chlorofiber: Not easy to burn, has the advantages of good warmth retention, water resistance, corrosion resistance, etc., commonly used in knitted underwear, wool Velvet, industrial filter cloth, work clothes, non-combustible curtains and carpets, etc. Polychloropropylene fabric has good electrostatic insulation and can be blended with other fibers to make underwear with a therapeutic effect on rheumatism. The disadvantage is that the softening point is very low. It usually starts to soften and shrink at 60~70℃. Therefore, you should be more careful when washing and ironing, and try not to iron chlorine fiber fabrics.






