
Spandex was first developed by Bayer in Germany and put into mass production by DuPont in the United States. Due to immature technology and insufficient market development, it has not been able to be mass-produced. It was not until the end of the 20th century that it was widely used in clothing fabrics. In the past 10 years, covered yarns, core-spun yarns, and twisted yarn fabrics of spandex and other fibers have developed greatly.
The composition of spandex
Polyurethane fiber is a kind of polyurethane fiber. The main component is block copolymer fiber. Macromolecules are composed of soft and hard segments.
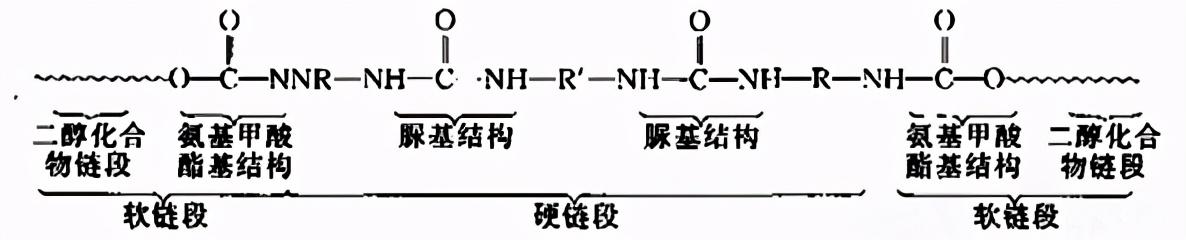
The soft segment is composed of amorphous polyester or polyether, with a very low glass transition temperature and is Highly elastic, when stretched at room temperature, the fiber can produce many large elongation deformations and has excellent resilience.
The hard segment is composed of diisocyanate that is crystalline and can undergo transverse cross-linking. Suanran has a short segment, but due to Containing a variety of polar groups, intermolecular hydrogen bonds and crystallinity play a cross-linking role between macromolecular chains, which can provide the necessary junction conditions for the substantial elongation and rebound of soft segments (organizing intermolecular relative slip), which can also give the fiber a certain strength.
The structure in which soft and hard segments coexist gives polyurethane fiber high elasticity and unified strength.
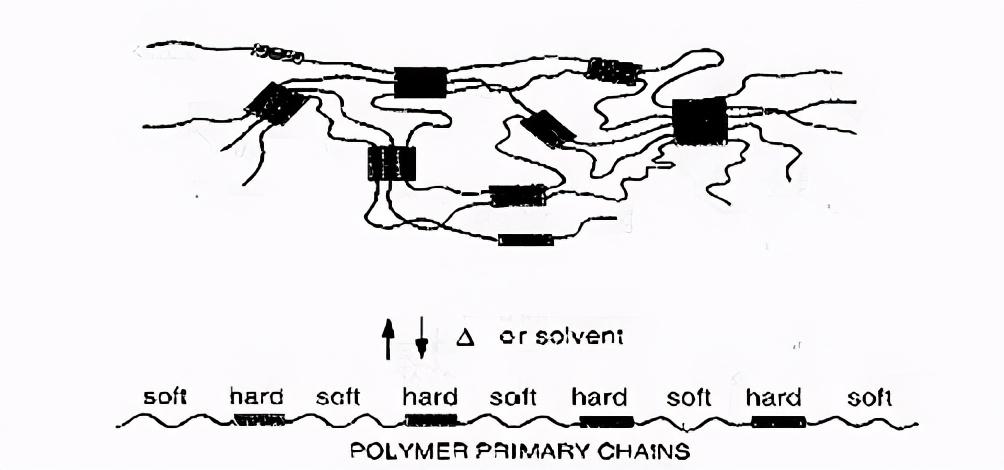
△ Schematic diagram of spandex molecular morphology
According to the molecular structure of the soft segment, spandex is divided into polyether spandex and polyester spandex. The main raw material of polyether spandex is polyether glycol (PTMEG), and the main raw material of polyester spandex is polyether glycol (PTMEG). It is polyester glycol (PEG). At present, most of the polyether spandex on the market is polyether spandex (the main raw materials are PTMEG and pure MDI).
Performance of spandex
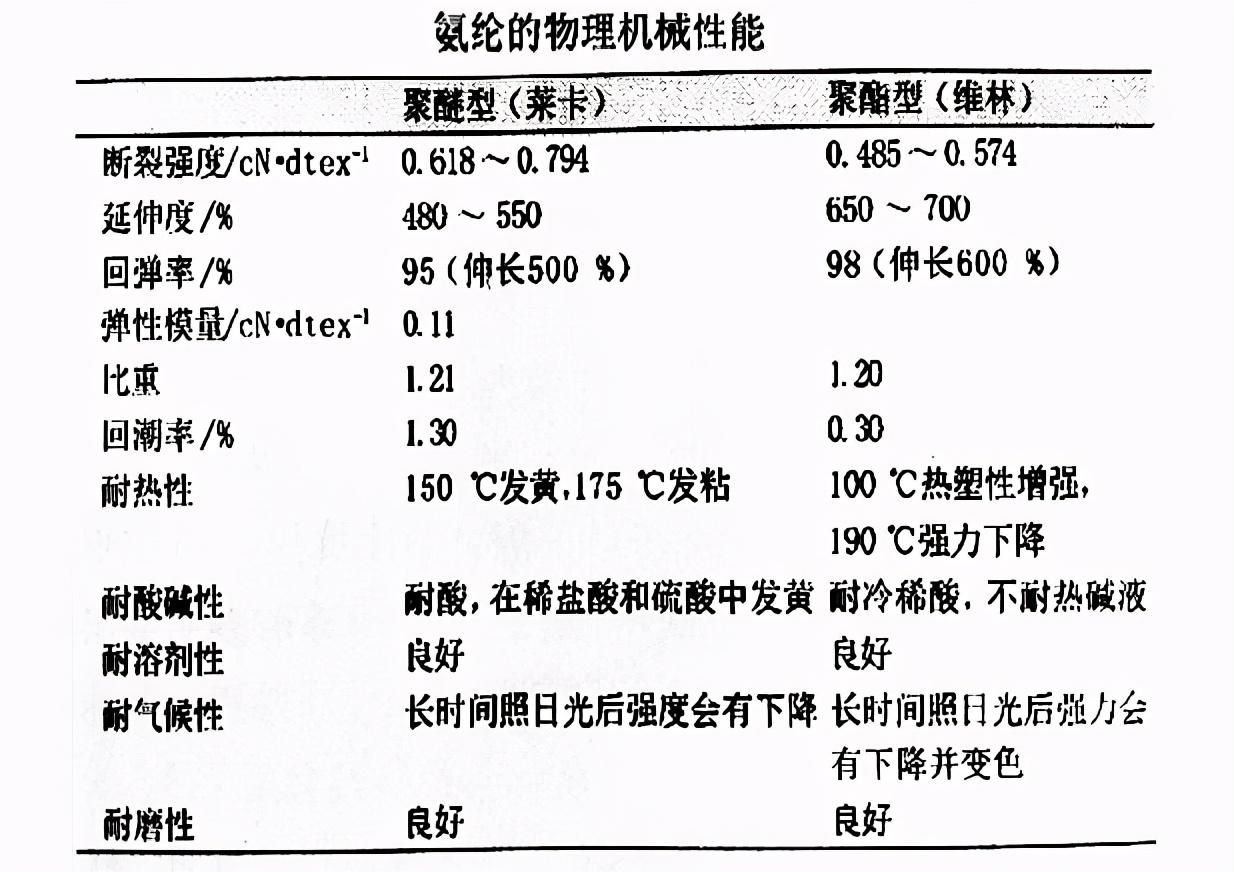
Elastic
Spandex fiber It has great elasticity and can generally be stretched to 4 to 7 times its original length. Under 2 times of stretching, its recovery rate is almost 100%. When stretched to 500%, its resilience rate is 95 to 99 %, which is beyond the reach of other fibers. Generally speaking, in the molecular structure of spandex fiber, the greater the molecular weight of the soft segment, the stronger the elasticity and rebound rate of the fiber. Polyether spandex has higher elasticity and rebound rate than polyester spandex; chemically cross-linked spandex The rebound ability is better than that of physical cross-linked type.
Strength
Because spandex is elastic, the strength cannot be tested in the same way as other fibers. When the fiber is stretched to its maximum length, the fiber becomes thinner, and the strength measured at this fineness is the effective strength. Due to the different structures of spandex, its strength is about 4~5cN/dtex, while the breaking strength is 0.44~0.88cN/dtex in dry state and 0.35~0.88cN/dtex in wet state. Since the hygroscopicity of spandex fiber is extremely low (0.3% ~ 1.3%), the plasticizing effect of water on spandex is not obvious, so its wet strength is only slightly lower than the dry strength. When the breaking strength of spandex fiber is close to 0.88cN/dtex, its elongation can reach 350% to 600%. Of course, spandex has a large breaking elongation and a large breaking work.
Heat resistance
The softening point of spandex is 205~210℃ and turns yellow at 150℃ , the strength decreases at 190℃ and even becomes sticky. Therefore, the general setting temperature of spandex fabric is preferably no more than 175~180℃. Due to the different organizational structure of the fabric and the different winding methods of spandex and other fibers, the setting temperature of generally covered yarn fabrics does not exceed 180°C, the setting temperature of thin core-spun yarn fabrics can reach 190°C, and the setting temperature of thick core-spun yarn fabrics can reach 195°C. ~210℃. Of course, the setting temperature depends on the shrinkage and elasticity requirements of the finished product. Domestic general customers do not have quantitative indicators for the elasticity of finished products. They only require the finished fabric to be slightly elastic, so the setting temperature is only controlled based on the shrinkage of the finished product. If the finished product has elasticity index requirements, the elastic loss of the fabric should be controlled throughout the process. When designing a process, first�After desizing the gray fabric, loosely wash it with water, measure the elastic recovery of the gray fabric (between about 25% and 35%), and then develop an effective process according to the elasticity requirements of the finished product.
Dyeing performance
For core-spun yarn, covered yarn and twisted yarn, because after dyeing Spandex is almost entirely covered by external fibers, so it is generally not necessary to consider whether the spandex is colored or not. However, spandex itself can be dyed with direct dyes, vat dyes, acid dyes, disperse dyes, reactive dyes, etc. However, the color fastness of direct dyes and reactive dyes is poor (especially in dark colors). If the bare yarn of spandex fiber or the spandex fiber is not completely covered by the external phase fiber, the dyeing of spandex must be considered.
Chemical resistance
Spandex is resistant to most acids, alkalis and chemical solvents, especially polyethylene Ether type spandex. Whether it is core-spun yarn, covered yarn or twisted yarn, during dyeing and finishing processes such as scouring, bleaching, and mercerization, most of the spandex has been covered by the external phase fiber, and the exposed surface area is very small, so the dyeing of the external phase fiber can be used. The whole processing technology.
Application of spandex
The excellent properties of spandex fiber raw materials make the fabric comfortable to wear and able to It is suitable for the bending needs of body parts, so that the clothing has little binding force on the body. At the same time, the fabric also has good anti-wrinkle and wrinkle-free properties, and the wrinkle setting ability is permanent. It is mainly used to manufacture various sportswear, swimming suits, skating suits, golf and other sportswear; as well as the belt-tightening parts of various special clothing such as astronaut suits, flight suits, work clothes; women’s tights and bodybuilding clothes. , underwear, bras, pantyhose, girdle, high-elastic socks, gloves, jackets, skirts and other women’s products; elastic corduroy, elastic labor cloth, elastic wool gabardine and wool tweed clothing materials; furniture and car seats outer covering decorative fabrics Fabrics; in medicine, various auxiliary equipment such as surgical elastic bandages, leather tubes, artificial organ materials, etc.







