1. Fabric weave
Woven fabric is It is composed of two sets of yarn systems, warp and weft yarns, which are perpendicular to each other, and are interwoven with each other on the loom according to certain rules. The warp and weft yarns are intertwined with each other, and the law of their ups and downs is the fabric structure.
2. Warp and weft
The length parallel to the edge of the cloth is called the piece length, and the direction of the piece length is the warp direction of the fabric. The length perpendicular to the edge of the fabric is the width, and the direction of the width is the weft direction of the fabric. The yarns used in the warp direction are called warp yarns, and the yarns used in the weft direction are called weft yarns.
3. Organizational points
The points in the fabric where the warp and weft yarns overlap are called weave points; the weave points where the warp yarns are on top and the weft yarns are on the bottom are called warp weave points (warp floating points); the points where the weft yarns are on top and the warp yarns are on the bottom are called weft weaves Point (latitude float).
4. Floating length
The length of yarn of one system floating on the yarn of another system is called floating length. It is divided into warp float and weft float.
5. Complete organization
When the ups and downs of warp and weft points reach a cycle, the unit formed is called a complete organization, or a tissue cycle.
6. Complete number of yarns
The number of all warp yarns in a complete weave is called complete warp yarns, represented by Rj; the number of all weft yarns in a complete weave is called the complete weft yarn count, represented by Rw. The number of warp yarns and weft yarns that constitute a weave cycle can be equal or different. The larger the number of yarn loops in the weave, the more complex and diverse the patterns may be. However, if the number of circulating yarns is the same, the fabric structure is not necessarily the same.
In an organization In the cycle, if the number of warp weave points and weft weave points are the same, it is called the same-plane weave; if the number of warp weave points is more than the number of weft weave points, it is called warp weave; if the number of weft weave points is more than the number of warp weave points, it is called weft weave.
7. Feishu
In a complete weave, the number of yarns in another system separated between corresponding weave points on two adjacent yarns in the same system is called the flying number, represented by “S”.
bySj (Sj): In a complete weave, the number of weft yarns separated by corresponding weave points on two adjacent warp yarns.
Weft flying number (Sw): In a complete weave, the number of warp yarns separated between the corresponding weave points on two adjacent weft lines.
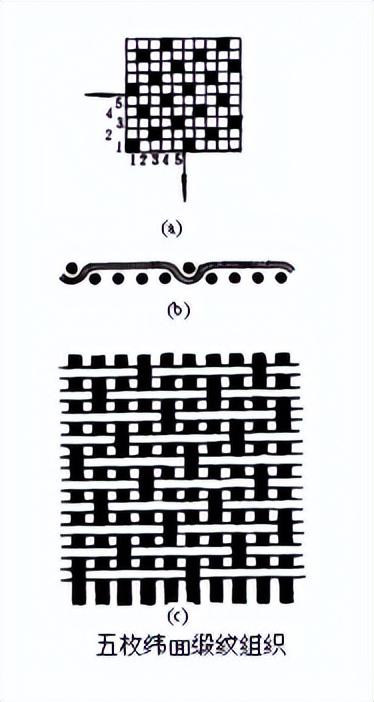
Use of satin weave: Since the interweaving points are far apart, the separate weave points are two Covered by side floating long threads, the floating long threads are long and numerous, so there is an obvious difference between the front and back of the fabric. No interweaving points can be seen on the front, and it is smooth and even. The fabric is soft, shiny and has good drape. It has poor wear resistance and is easy to rub. Damage and fluffing. The larger the number of circulating yarns in the satin weave, the longer the yarn floating length on the surface of the fabric, the better the gloss, the softer the feel, but the worse the fastness.
In order to highlight the effect of warp satin, the warp density should be greater than the weft density. In general , the ratio of warp and weft density is 3:2. Also in order to highlight the effect of weft satin, the ratio of warp and weft density is 3:5. In order to ensure that satin fabric is bright and soft, untwisted or less twisted fabric is often used Yarn. As long as the warp yarn of the warp surface satin pattern can withstand the mechanical force during weaving, its twist should be reduced. The twist of the weft yarn of the weft surface satin pattern should be appropriately reduced so as not to affect the smooth progress of weaving too much. Yarn The twist direction also has a certain influence on the appearance of the fabric. If the twist direction of the warp yarns of the warp surface satin or the weft surface satin weave is consistent with the grain direction of the satin weave points, the surface of the fabric will be bright, such as horizontal satin. Vice versa. , the texture and luster on the satin surface will be weakened, such as Zhigong cloth, etc.
Please see the following satin weaves
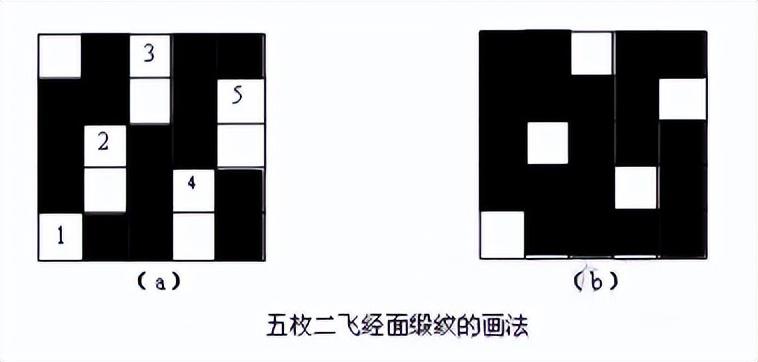
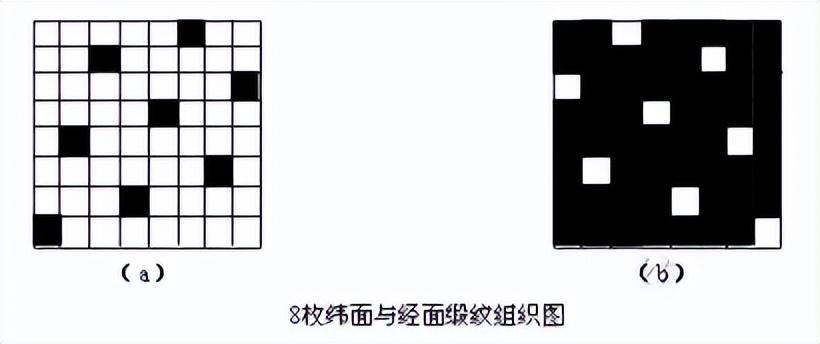

Enhanced Satin
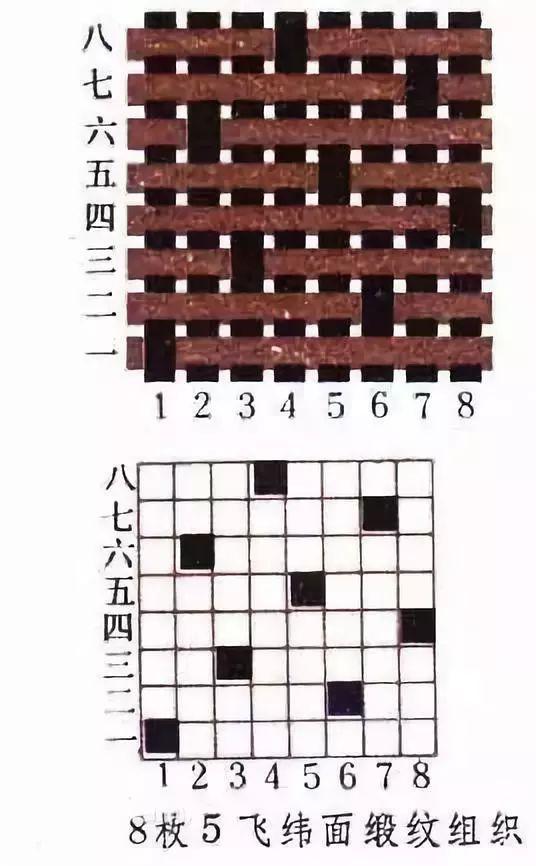
Weft satin
Satin texture








