
Wool fabric has a rich texture, smooth and drapey feel It has the characteristics of good sex, elegant wear, lightness and comfort, and is favored by consumers. But how do these wool fabrics, which are favored by consumers, translocate to us after being processed by dyers? Today let’s talk about wool fabrics with you.
The structure of wool
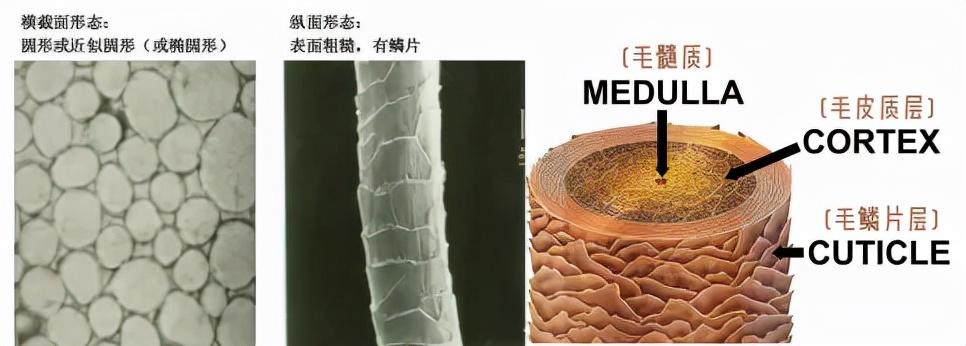
Wool is an elongated solid cylinder with a curly shape and a rough surface. It is composed of scale layer, cortex layer and medulla layer. The finer the wool, the more scales it has. Because the scale layer stretches outward and protrudes, the number of scales increases. The friction between fibers leads to mutual restraint and felting, and the cohesion force is strengthened under hot and humid conditions. The cortex layer is composed of two parts: the normal cortex layer and the paracortical layer. As the main component of wool, it determines the physical, mechanical and chemical properties of wool fibers. The medulla layer is an opaque loose substance; the more medulla there is, the straighter and rougher the wool will be, and the worse the quality will be.
Finishing technology of wool fabrics
Due to the wide variety of wool fabrics, there are certain differences in the finishing processes. For example, smooth fabrics may Involving:Green repair → singeing → washing → boiling → dyeing → water absorption → drying – intermediate inspection → cooked repair → brushing → shearing → wet parking → steaming → voltage; And velvet The surface fabric involves: Preparation → Washing → Dehydration → Shrinking → Washing → Dyeing → Dehydration → Drying → Inspection → Repair → Raising → Brushing and shearing → Steaming and brushing → Steaming,So today Discuss the purpose and principles of general finishing processes.
01 Carbonization
Purpose: to remove plant impurities in wool. Principle: The difference in acid resistance between wool and cellulose impurities is used to remove impurities. Acid promotes the hydrolysis of cellulose impurities, making them brittle, and removes them by rolling and washing; while -NH2 on the wool absorbs H+ and begins to absorb acid at pH=5, reaching saturation at pH=1, without damaging the wool. If acid absorption continues, the wool main chain will be hydrolyzed, so the acid concentration and temperature must be strictly controlled during the production process.
02 Wash it
Purpose: Purify and improve the feel. Principle: Generally, surfactants are used to wash the wool to remove impurities and improve the feel. Wool fabrics are constantly moving and squeezing during washing, which has a certain shrinking effect. When the fabric is required to feel plump, the washing time can be up to about 2 hours. Generally, the washing time for wool fabrics is 45 to 90 minutes. After washing, wash it with warm water of about 40℃.
03 Boiling and Steaming
Purpose: To make the fabric dimensionally stable, the fabric surface is flat, the luster is natural, the hand feels soft and elastic. Principle: Wool fibers are subject to uneven external forces during spinning and weaving, causing internal stress in the fabric. Under hot and humid conditions, the internal stress relaxes, resulting in uneven shrinkage. During processing, new cross-links are re-established at new positions to produce a styling effect.
04 denim
Purpose: Under certain temperature conditions, after the wool fabric is moistened by the wetting agent, under the repeated action of mechanical external force, the fibers bite and entangle with each other, causing the fabric to shrink, increase the thickness, and produce a layer of fluff on the surface to cover up the texture. crafting process. Principle: The friction coefficient of wool moving against the scales (pointing to the hair tip) is larger than the friction number moving along the scales (pointing to the hair roots), which is called the directional friction effect. When the shrinkage agent is present, repeated random external forces force the wool to shrink and move along the scales. The wool roots bite each other and the fiber tips are free to cover the surface of the fabric. Since the arrangement of the fibers is relatively disordered, the result of the movement is that it tends to shrink.
05 anti-felting
Purpose: to reduce the shrinkage of wool fabrics, provide dimensional stability to the fabrics, and reduce pilling. Principle: By reducing the directional friction effect, the inherent elasticity of wool is improved and the wool is restricted from moving between each other. Anti-felting is usually achieved by destroying the scale layer of wool and depositing polymers on the surface of the fabric.
Principles and processes of dyeing wool fabrics
Dye classification
Acid dyes and wool reactive dyes are generally used for dyeing wool fabrics
01
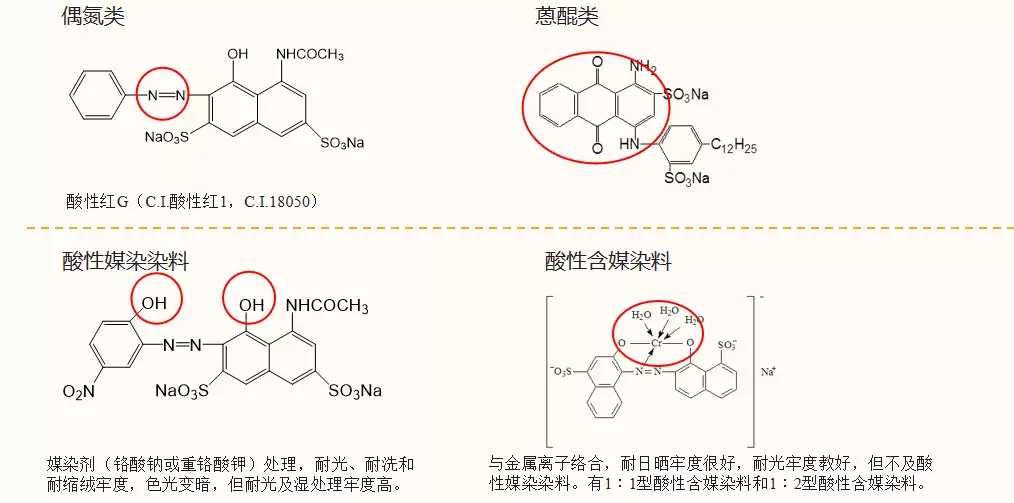
Acidic Dyes
Contain water-soluble groups, low directivity, and can be used in acidic, weakly acidic or Dyes for dyeing proteins and polyamide fibers in neutral dyeing solutions.
02
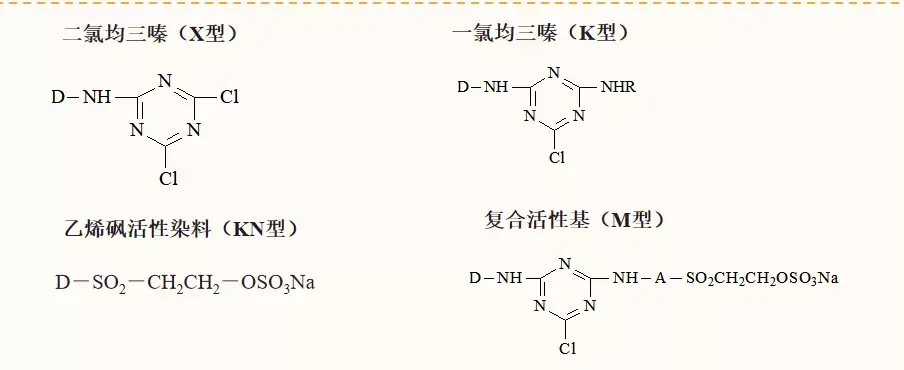
Reactive dyes for hair
Dye molecules have Reactive group, the reactive group can react chemically with the hydroxyl (-OH), amino (-NH2), etc. on the fiber to form a covalent bond. The general formula of the dye structure: S-D-B-Re
Dyeing principle
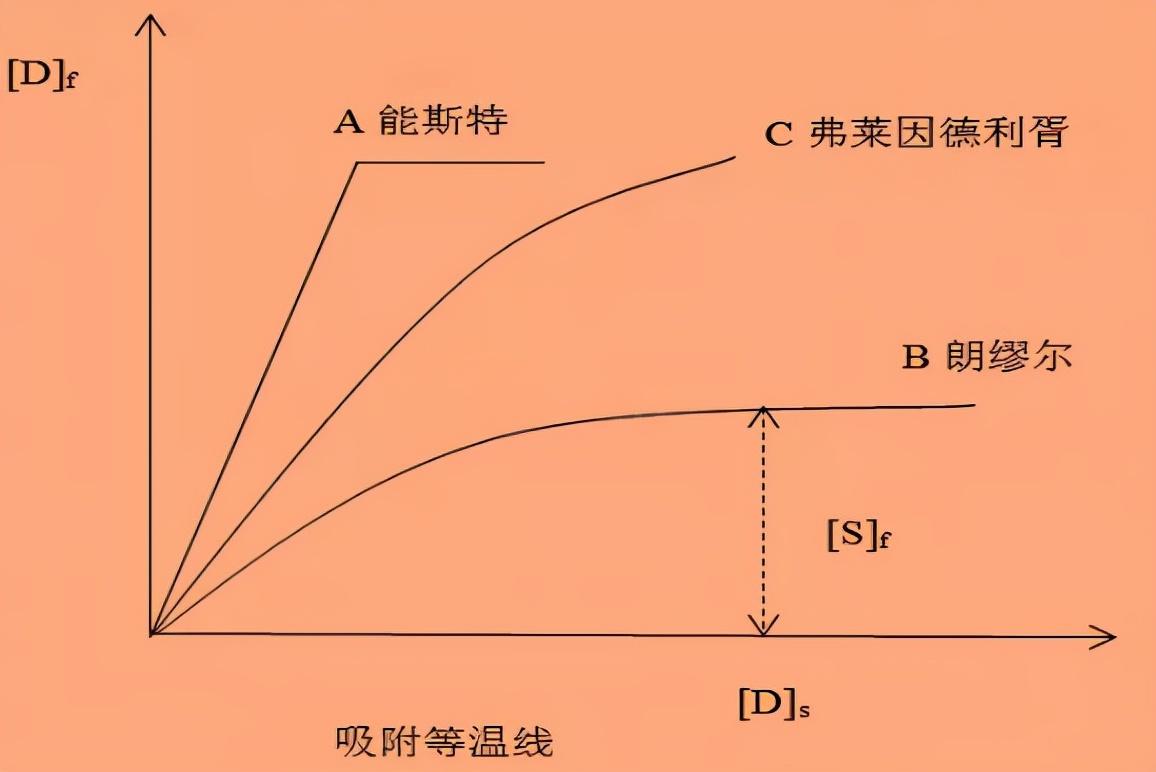
The dyeing of protein fibers with acidic dyes is based on the pore diffusion model;
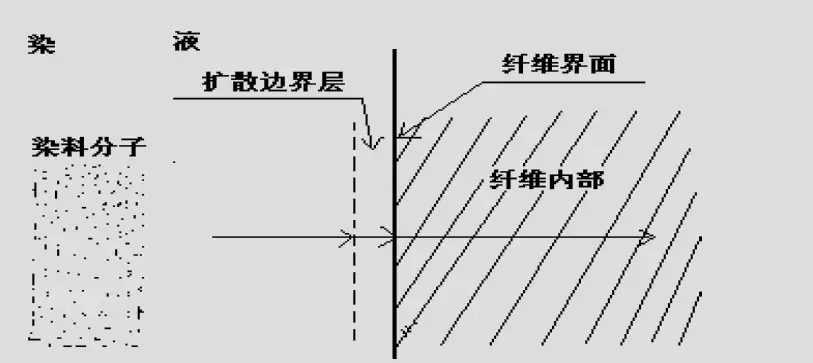
[pore diffusion model↑]
Strong acid bath, Langmuir type adsorption;
Weakly acidic bath: pHpI Freundlich type adsorption;
Neutral bath dyeing: pH=6~7, Freundlich type adsorption. (pI: When the number of positive and negative ions on the fiber macromolecules is equal, the net charge of the fiber is zero, that is, it is electrically neutral and in an isoelectric state. The pH value of the solution at this time is called the isoelectric point pI of the fiber).
Physical meaning:The adsorption isotherm can be used to infer the dyeing mechanism of the dye and control the dyeing process. The slope change can determine the reasonable dosage range of the dye and improve the dye utilization rate.
Dyeing process
Acid dye dyeing in weak acid bath dyeing
Dyeing formula:
Dye: X%
Yuanming powder: 1-2g/L
Acetic acid 60% (pH=4.5-5.5):1-3%
Leveling agent: 0.5-1.5%
01
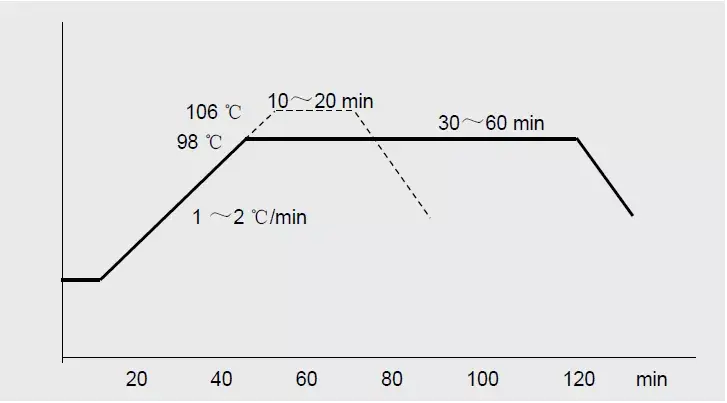
Temperature
60℃ , T↑, the disulfide bond is opened and the dyeing rate increases. Control the temperature in the early stage to improve level dyeing; dye at 95~100℃ in the later stage and keep it warm for 30~60 minutes.
02
Leveling agent
Neutral electrolyte Cl- , SO42-. Principle: competitive dyeing, ion exchange with dye ions to achieve level dyeing effect.
style=”color: #FF0000; –tt-darkmode-color: #FF0C00;”>Dyeing process
Weakly acidic bath dyeing Acid dye dyeing
Dyeing formula:
Dye: X%
Yuanming powder: 1-2g/L
Acetic acid 60% (pH=4.5-5.5 ):1-3%
Leveling agent: 0.5-1.5%
01
Temperature
60℃, T↑, disulfide When the key is turned on, the dyeing rate increases. Control the temperature in the early stage to improve level dyeing; dye at 95~100℃ in the later stage and keep it warm for 30~60 minutes.
02
Leveling agent
Neutral electrolyte Cl- , SO42-. Principle: competitive dyeing, ion exchange with dye ions to achieve level dyeing effect.






