Woven fabric is a fabric formed by interweaving warp and weft yarns vertically with each other. Knitted fabrics are made by using knitting needles to form yarns or filaments into coils, and then stringing the coils together. Non-woven fabric refers to a fiber layer composed of a certain orientation or random arrangement without traditional spinning, weaving or knitting processes, or the fiber layer is intertwined with yarn, and is wrapped through mechanical hooking, stitching or chemical, hot melt, etc. Fabrics made by joining together.
Woven fabrics
Two systems (or directions) The fabric formed by the yarns being perpendicular to each other and interlaced according to certain rules is a woven fabric (also called a woven fabric).
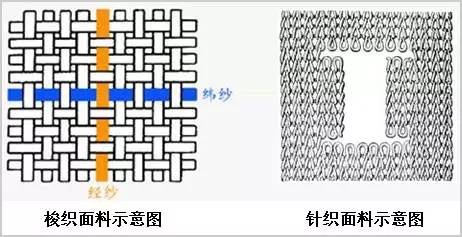
△The principle difference between woven and knitted
The basic organization is the simplest and most basic organization among all types of organizations, and is the basis for various changes and fancy organizations Base. The basic weaves include plain weave, twill weave and satin weave.
Plain weave
Plain weave is one of all fabric weaves The simplest kind. Its organizational rule is one up and down, and the two roots alternate to form a complete organization.
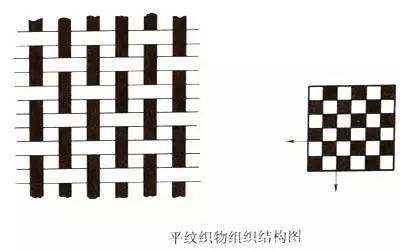
Features
The plain weave has the most interlacing points of warp and weft yarns, and the yarns buckle more, so The fabric surface is flat, the body is stiff, the texture is firm, and the appearance is tight, but the feel is hard and the elasticity is low. In actual use, various methods can be used according to different requirements, such as different thicknesses of warp and weft yarns, changes in warp and weft yarn density, and different combinations and configurations of twist, twist direction and color, etc., to obtain various special products. appearance effect.
Common plain weave fabrics
Plain weave fabrics are widely used in cotton, wool, silk, and linen fabrics, such as various plain cloths with flat surfaces and textures. Fine spun fabrics, poplin with clear diamond-shaped particles, grosgrain with obvious concave and convex horizontal stripes, seersucker and georgette with crepe effect, as well as velvet, palis, thin tweed, flannel, etc. with hidden grid effect .
Twill weave
The characteristic of twill weave is that the short floating lengths in the warp direction or the short floating lengths in the weft direction are arranged in a stepped manner, forming a continuous diagonal line on the surface of the fabric. The movement of each warp yarn in its organization is the same, but the starting point is different.
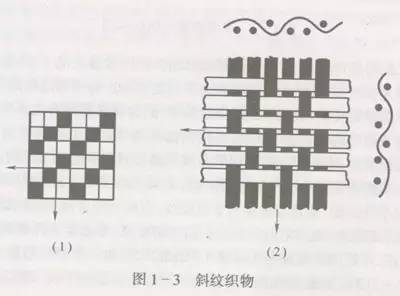
Twill weave is divided into left twill and right twill according to different diagonal grains.
Left twill: inclined from the upper left to the lower right, represented by “↖”;
Right twill: from the upper right direction The lower left tilt is represented by “↗”.
Twill weave is divided into single-sided twill and double-sided twill according to the different order of the latitude and longitude weave points.
Single-sided twill: The front and back sides have different latitude and longitude weave points;
The latitude and longitude weave points are the same but the order of ups and downs is different.
Double-sided twill: The organization points and the order of rising and falling are the same on both sides, but the diagonal directions are different.
Single-sided twill can be divided into warp twill and weft twill.
Warp twill:Warp weave points>Weft weave points
Weft twill:Weft weave points>Warp weave points
Common twill fabrics
Common twill fabrics have flat texture Twill, serge, khaki, gabardine, etc. with prominent gongzi.
Satin weave
Tissue parameters and characteristics
Satin weave is the most complex of the basic tissues. Its characteristic is that each warp yarn (or weft yarn) has only one single weave point (warp weave point or weft weave point). There is a certain distance between the separate weave points on two adjacent yarns and is separated by two Covered by warp floating threads or weft floating threads, the surface of the fabric is almost entirely composed of a kind of warp floating threads or weft floating threads, so the cloth surface is smooth and even, with good luster and soft texture.
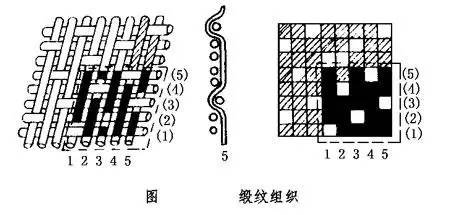
Satin weave has a wide range of applications. In cotton and wool fabrics, five-piece satin weaves are mostly used to obtain Zhigong, Henggong, Henggong satin, etc.; in silk fabrics, eight-piece satin weaves are mostly used to obtain various plain satins and floral satins with better luster. Satin or satin patterned fabric.
Change weave
Change weave is to change the original weave (such as changing the circulation of yarn Various derived structures obtained from the number, floating length, flying number, twill line direction, etc.). Changes in weave can be divided into three categories: plain weave change (including heavy flat weave, square weave, etc.), twill change weave (including reinforced twill, composite twill, angle twill, mountain-shaped twill, diamond twill, etc.)It has high performance and is widely used in clothing fabrics, artificial fur base fabrics, velvet linings, etc.
Yarn-type stitch-bonded structure non-woven fabric
Yarn layer – stitched yarn-type stitch-bonded non-woven fabric
It is layered with warp and weft yarns, and the stitch-bonded yarns are woven according to the warp and flat weave to reinforce the yarn layer. Textiles. The fabric has the appearance of organic fabrics and knitted fabrics, has good dimensional stability and high strength, and is suitable for outerwear fabrics.
Yarn layer – terry stitched non-woven fabric
The weft yarns are laid up to form a net, which is reinforced by a chain structure formed by stitching yarns. The terry yarn is inserted in sections in the stitching area to give the cloth a raised terry shape. Can be used for decorative fabrics, clothing materials, etc.
Application fields of non-woven fabrics Although the rise of non-woven fabrics is only half a century old, it is developing rapidly. Compared with ordinary woven fabrics, due to its unique structure and processing methods, it has broad application prospects. Its products have been widely used in many fields such as civilian clothing, decorative fabrics, industrial fabrics, medical materials, military industry and high-end technology. There are hundreds of products developed, such as various clothing linings, curtains, Disposable products for medical care, geotextiles, filter cloths, cushions, wall coverings, carpets, baby diapers, packaging materials and crop insulation sheds, etc.







