Spinning is a very ancient activity. Since prehistoric times, humans have known how to spin short fibers into long yarns and then weave them into cloth. Spinning: The process of spinning textile fibers into yarn by physical or mechanical means.

Basic principles of spinning
01
Opening and cleaning ( Qinghua)
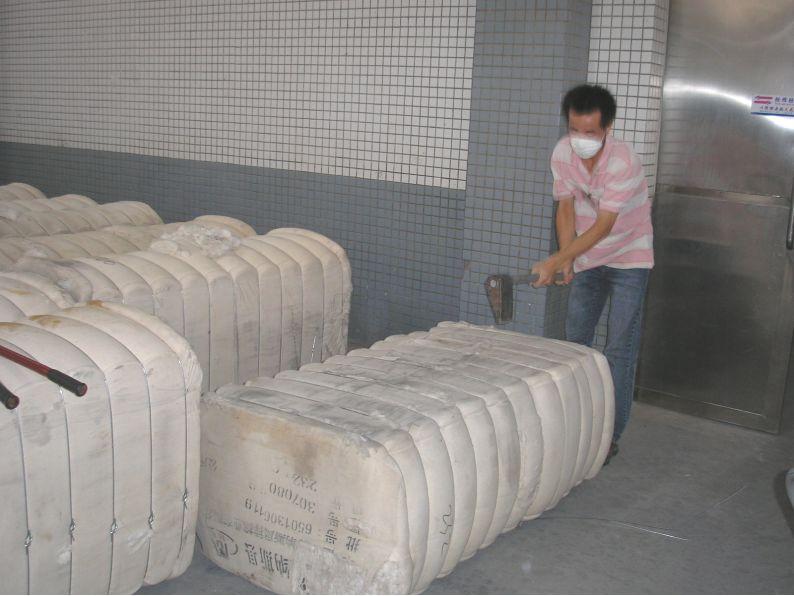
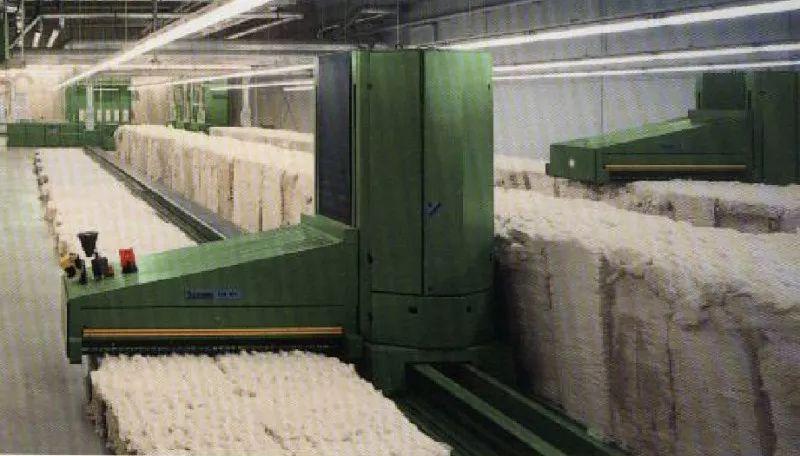


△Straight-line cotton picking machine
Main tasks
Opening – opening the massive fibers in the compressed chemical fiber package into small pieces or small fiber bundles.
Impurity removal – remove some impurities from raw materials.
Mixing – uniformly mixing fibers of various properties.
Rolling – making uniform chemical fiber rolls for use in the carding process.
02
Carding
Feed the cotton roll into the carding machine, and obtain the sliver after carding.
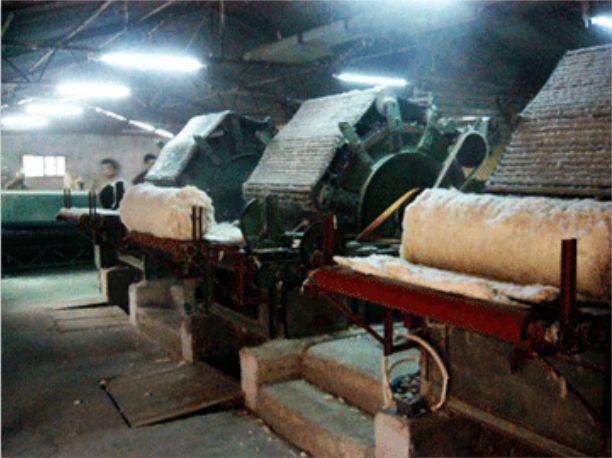

△The cotton laps produced in the blowroom process are fed to the carding machine
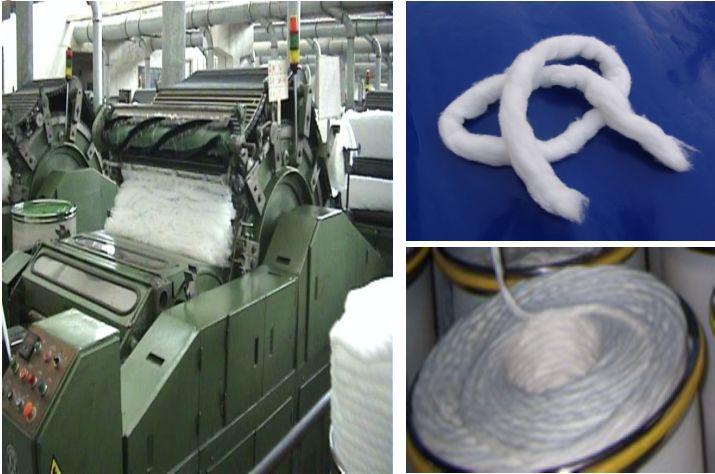

Main tasks
Carding – Obtaining single fibers
Impurity removal – Removing impurities and short fibers
Mixing – mixing between single fibers
Striping – making a uniform sliver
03
Drawing
In order to improve the uniformity of the slivers, 6 to 8 slivers are combined and fed into the draw frame, and one sliver is obtained through roller drafting Notes.

Main tasks
Leveling – improving the sliver quality Dry uniformity in order to obtain more uniform yarn;
Parallel – strive to make the fibers in the sliver more straight and parallel;
Mixing – mix various fibers as required;
Strips – pack them into strips as required in a sliver bucket for downstream use process production.
04
roving
p>
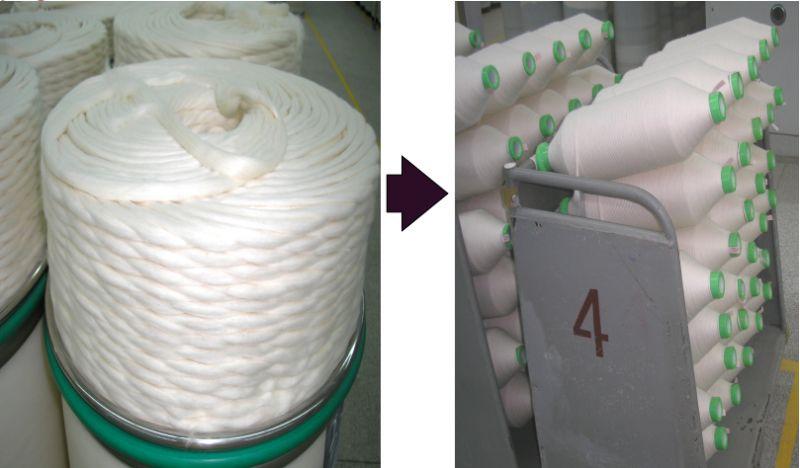

Main task
Drafting – lengthening and thinning the sliver Become a roving.
Twisting – adding a certain twist to the roving to increase its strength.
Winding – winding the twisted roving onto the bobbin.
05
Spinning yarn

Main task
Drafting – drafting the roving to the desired Required special number.
Twisting – adding a certain twist to the drawn yarn to make it have a certain strength, elasticity and luster.
Winding – winding into bobbin for easy transportation and post-processing.
06
Post-processing ( Winding, doubling, twisting)
Main tasks
Improve the appearance quality of the product by removing yarn defects and nep impurities through singeing, waxing, winding, etc., and improve the evenness and smoothness of the evenness.
Change the intrinsic properties of the product and improve the strength of the yarn through yarn doubling, twisting, etc.
Stabilize the structural state of the product, mainly stabilize the yarn twist
Make it into an appropriate package form for easy transportation and storage And further processing, such as making into cheese yarn, skein yarn or into large packages, small packages, etc.

▲Winding: 1. Extend the yarn to increase the yarn package capacity and improve the efficiency of subsequent processes. Productivity. 2. Remove defects and impurities on the yarn and improve the quality and strength of the yarn.

▲Double yarn: two or more single yarns combinedTogether.
▲Twisting: yarns are combined together, add a certain twist, and processed into strands.
Spinning technology system
In order to obtain yarns with different quality standards, different spinning methods and spinning systems should be adopted for different fiber materials.
Cotton spinning system
The raw materials used in cotton spinning production include cotton fiber and cotton-type chemical fiber, and its products include pure cotton yarn, purified fiber yarn and various blended yarns. In the cotton spinning system, according to the raw material quality and yarn quality requirements, it is divided into carding system, combing system and waste spinning system.
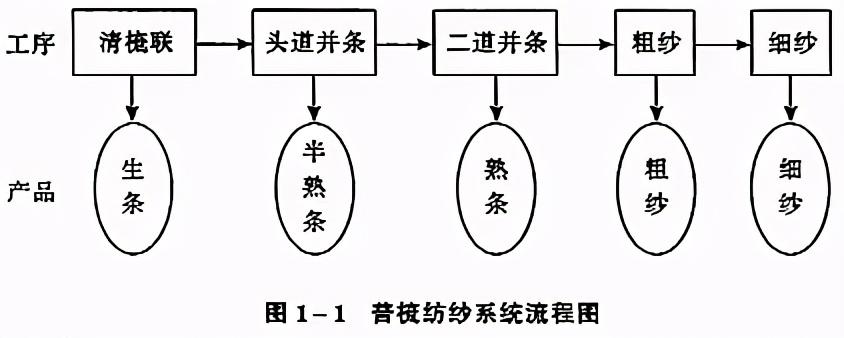
(1) Carding system
Generally used to spin coarse and medium special yarns for weaving ordinary fabrics. The process and names of semi-finished products and finished products are shown in Figure 1-1.
(2) Combing system
For combing system It is used to spin high-grade cotton yarn, special yarn or cotton and chemical fiber blended yarn. The process of the combing system and the names of semi-finished products and finished products are shown in Figure 1-2.
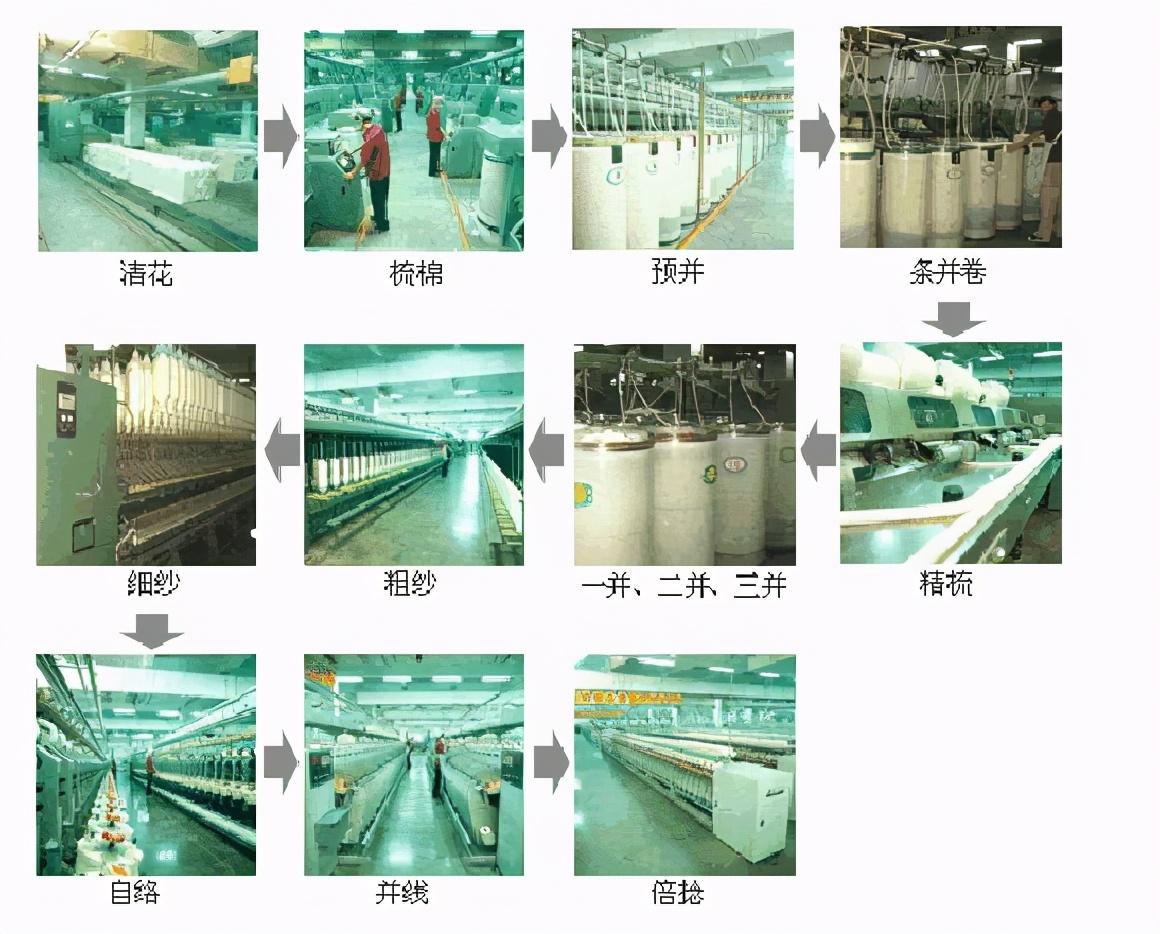
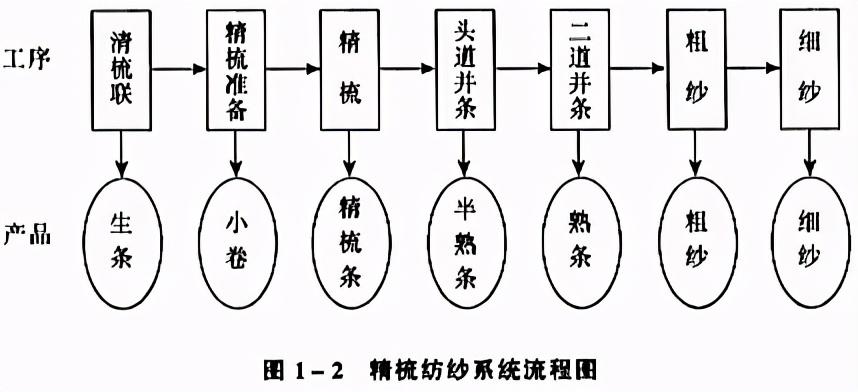

combed

Further remove neps, impurities and fiber defects in the fiber, and exclude a certain length The following short fibers are used to improve the uniformity and straightness of the fiber length and thin the cotton sliver to a certain thickness.
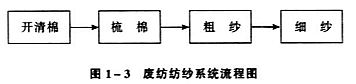
(3) Waste spinning system
The waste spinning system is used to process low-priced thick special cotton yarn. The process is shown in Figure 1-3.
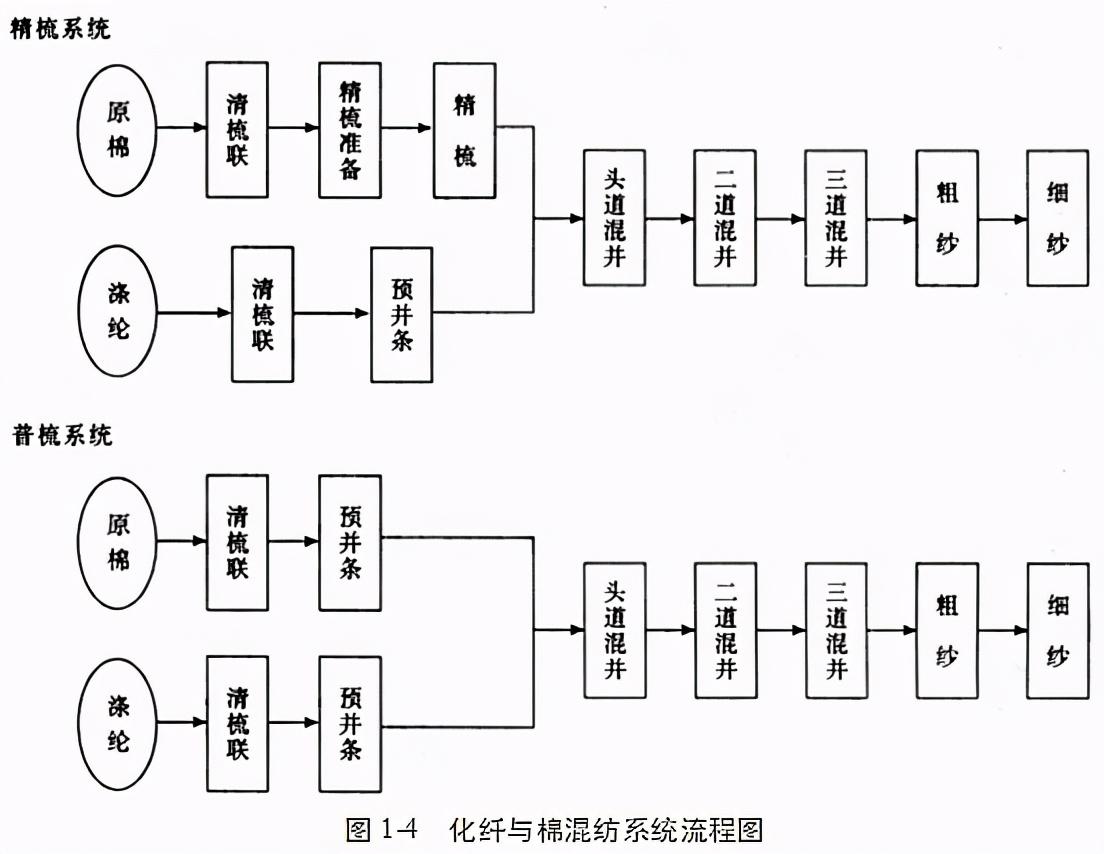
(4) Chemical fiber and cotton blending system
Polyester ( or other chemical fibers) and cotton, due to the different properties and impurities of polyester and cotton fibers, they cannot be mixed and processed in the love letter process. They need to be made into slivers from a grid and then mixed on the first draw frame (mixing). , in order to ensure uniform mixing, three drawings are required. The process flow of carded and combed spinning is shown in Figure 1-4.
Wool spinning system
The wool spinning system uses wool fiber and wool-type chemical fiber as raw materials and spins wool yarn, hairy chemical fiber blended yarn and pure chemical fiber yarn on wool spinning equipment.
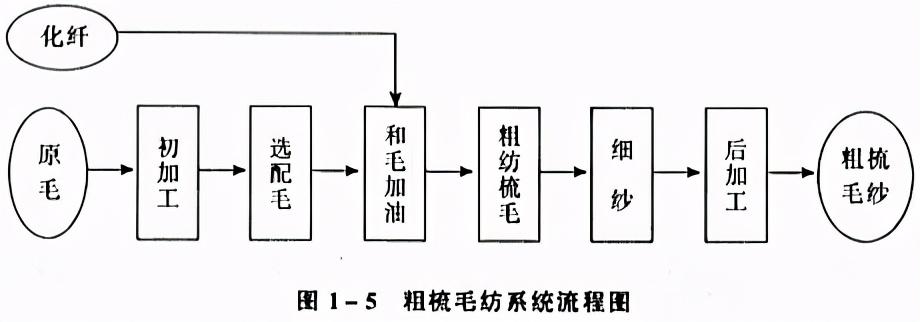
(1) Carding wool spinning system
The flow chart of the coarse wool spinning system is shown in Figure 1-5.
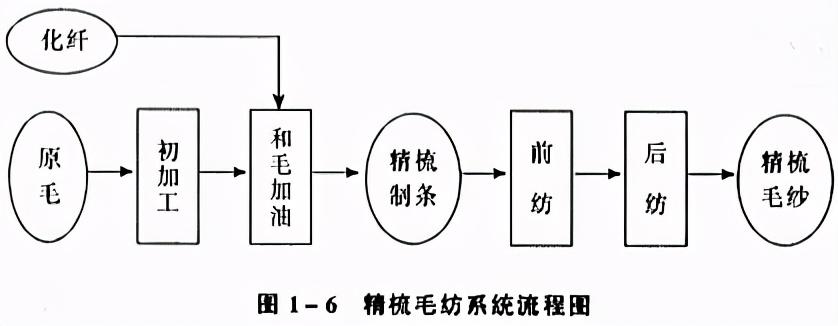
(2) Worsted wool spinning system
Worsted wool spinning The system has many procedures and long processes, and can be divided into two parts: straight strips and spinning. The spinning system process is shown in Figure 1-6.
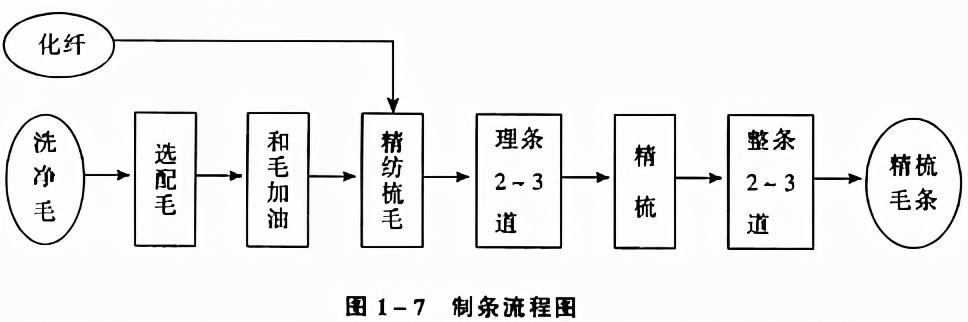
Combed strips are also called For top manufacturing, a separate factory can be set up, and the product (combed top) can be sold as a commodity. The top manufacturing process is shown in Figure 1-7.
Some combed wool mills do not The strip making process uses combed top as raw material, and the production process includes pre-spinning and post-spinning. Most factories do not yet have the strip dyeing and re-combing process of top dyeing and re-combing. Re-combing refers to the second time after top dyeing. The combing and recombing processes are similar to the strip making process. The flow of combed wool spinning system without recombing process is shown in Figure 1-8. In addition, there is a semi-combed spinning process system between combing and carding.
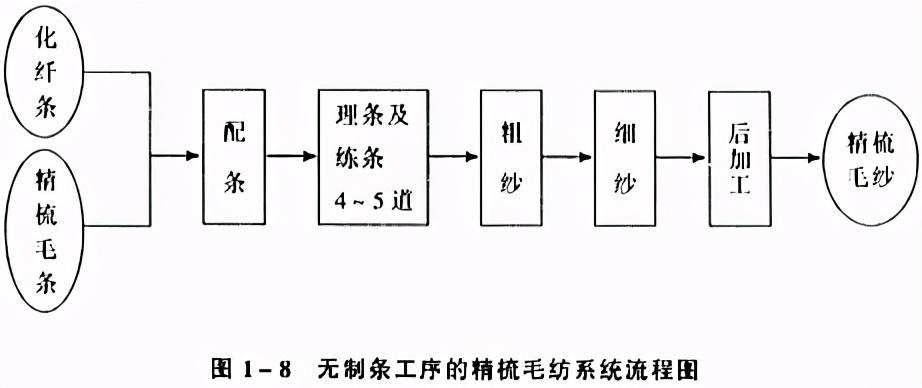
Line spinning system
There are three spinning systems of ramie, jute and flax.
(1) Ramie spinning system
Generally, the worsted wool spinning or silk spinning system is used, with only partial improvements in the equipment. Raw hemp must first be pre-processed into refined hemp, and the spinning process is shown in Figure 1-11; while short ramie and noiled hemp can generally be processed with a cotton spinning system.
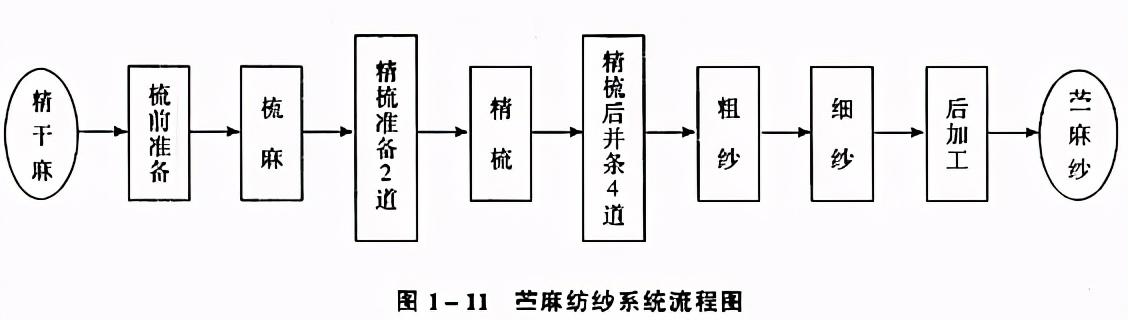
(2) Linen spinning system
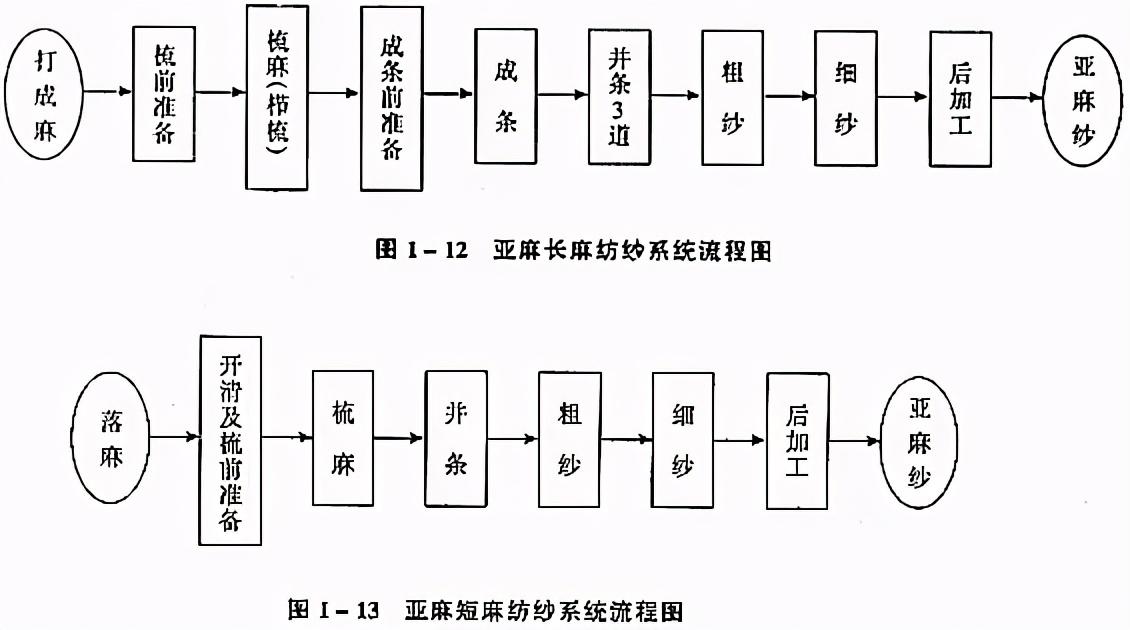
Flax spinning The raw material is flax, which is processed using the flax long linen spinning system. The spinning process is shown in Figure 1-12. Among them, the long linen roving must be scoured before being processed into spun yarn. The falling and returning hemp from long linen spinning enter the short linen spinning system, and its process is shown in Figure 1-13.
(3) Jute spinning system
Jute spinning The technological process is: raw materials → raw material preparation → carding → drawing → spinning.
“>Generally, the worsted wool spinning or silk spinning system is borrowed, and only partial improvements are made on the equipment. The raw linen must first be pre-processed into fine linen, and the spinning process is shown in Figure 1-11; while short ramie, falling ramie Linen can generally be processed using a cotton spinning system.

(2) Linen spinning system
The raw material of flax spinning is beaten into flax, which is processed using the flax long linen spinning system. The spinning process is shown in Figure 1-12. Among them, the long linen roving must be scoured and then Spinning yarn processing is carried out. The falling and returning hemp of long linen spinning enter the short linen spinning system, and the process is shown in Figure 1-13.

(3) Jute spinning system
The process flow of jute spinning is: raw materials → raw material preparation → carding → drawing → spinning.
p>







