Hemp fiber identification method
For hemp, a natural cellulose fiber, it has the same The chemical properties and macromolecular structure of hemp fibers can only be identified using microscopy and the unique appearance and morphological characteristics of different varieties of hemp fibers. The following is an analysis of the longitudinal and cross-sectional characteristics of various commonly used hemp fibers.
1
Rami
The longitudinal appearance of ramie fiber is flat or cylindrical, with flat shape being the main form. There is a curved bend, no curling. The fiber surface is smooth, with obvious bamboo knots and discontinuous cracks, and the fiber fineness is relatively uniform.
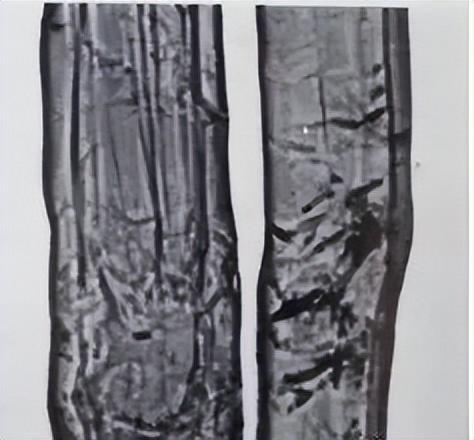

The cross-section of ramie fiber is elliptical Shape, with an oval or waist-round cavity, uniform cell wall thickness, and radial cracks.
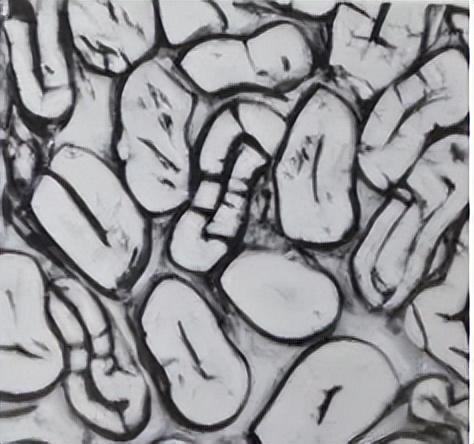
2
Linen
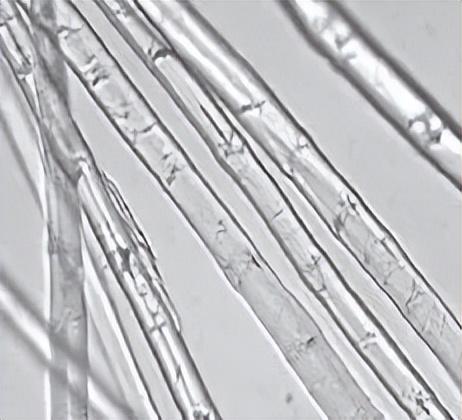
The longitudinal appearance of flax fiber is flat or cylindrical, mainly cylindrical. The fibers are straight and not curled. The fiber surface is smooth, with obvious bamboo knots, and some have grooves. The fiber strands are evenly dried.

The cross-section of flax fiber varies with flax It varies depending on the part of the stem. They are generally round, polygonal or oval in shape, with thicker cell walls and smaller central cavities.
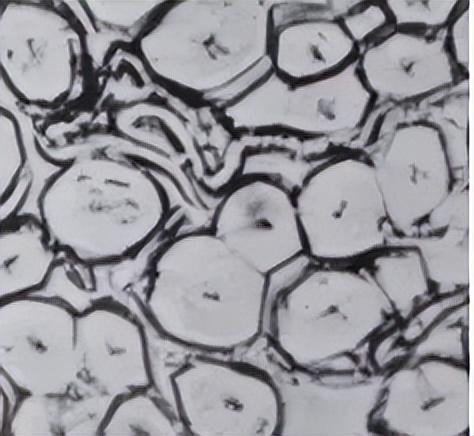
3
Marijuana
The longitudinal appearance of hemp fiber is complex and diverse, ranging from irregular cylindrical shapes to flat ribbons and prisms. Some have a natural twist that resembles cotton. The fibers have poor orientation and are entangled with each other. Some fiber surfaces are smooth and some are rough. There are bamboo joints but not obvious, and the fiber thickness is uneven. The head end of the fiber is blunt.
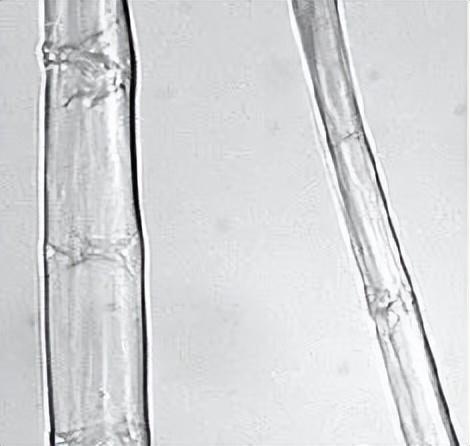
The cross-section of hemp fiber is very complex and mostly irregular. triangle, quadrilateral, hexagon, oblate, waisted circle or polygon.
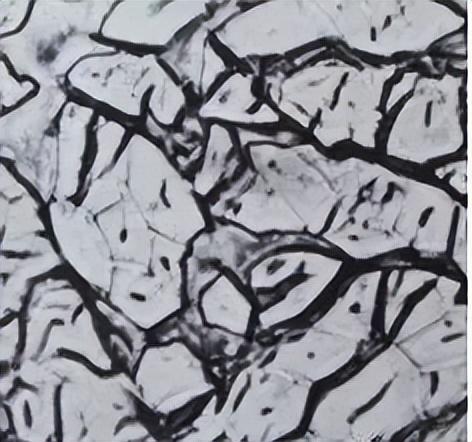

4
Jute
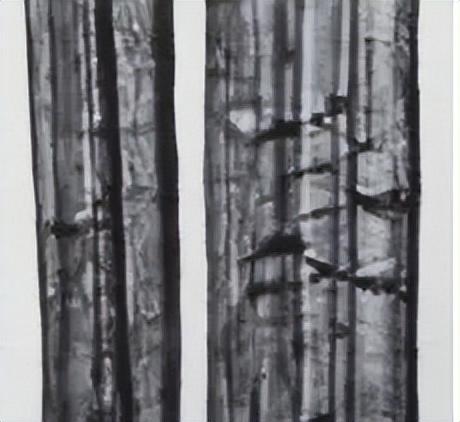
The longitudinal surface of jute fiber is straight, smooth and shiny. It is generally in the form of bundles, without distortion, and has a columnar structure. There are inconspicuous bamboo knots and fine continuous long stripes, and the fiber fineness is relatively uniform.

The cross-section of jute fiber is generally pentagonal or hexagonal , the middle cavity is oval or round, and the cell wall thickness is uniform.
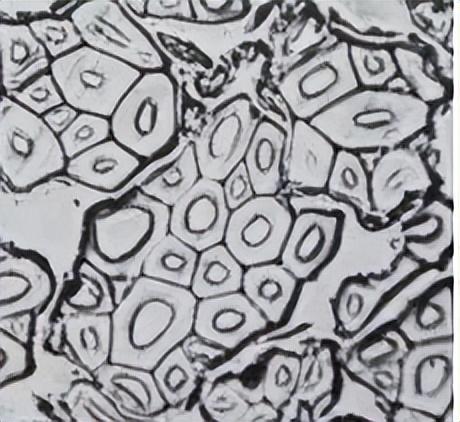

5
Apocynum
Apocynum fiber is slender, straight, smooth, round and transparent, with a silky luster. Generally, it has a regular cylindrical structure without distortion. There are unobvious bamboo knots and sparse long stripes, and the fiber fineness is relatively uniform.
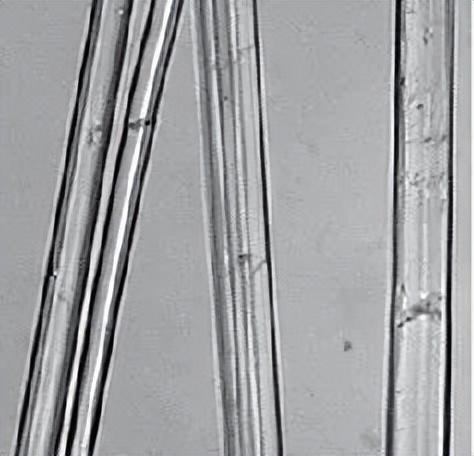
The cross-section of apocynum fiber is generally polygonal or elliptical Shape, with a larger middle cavity.
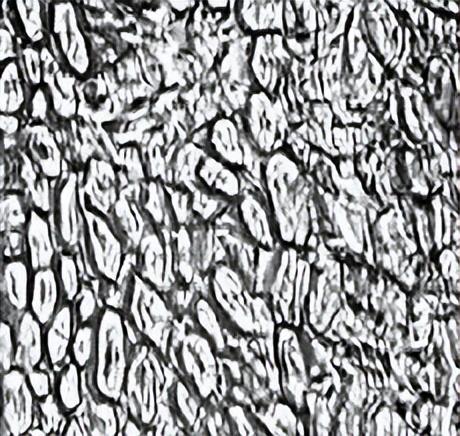

Hemp fiber Key points of identification
[Longitudinal cross-section form]
1. Stem shape
Ramie: Most are flat, some are cylindrical, arc-shaped, and even in thickness;
Flax: Most are cylindrical, some are flat, similar to ramie, and have a more uniform thickness;
Marijuana: messy, irregular Cylinder, partly flat ribbon, curled, much like cotton, with widely varying thickness;
Jute: more regular cylinder, mostly in bundles shape;
Apocynum: regular cylinder with even stems, very close to bamboo stems.
2. Bamboo Festival
Ramie: The knots are thicker and look like an X type, the bulges are not obvious, the spacing between knots is large, and they are sparsely distributed;
Flax: bamboo-like knots with obvious bulges between the knots The spacing is smaller and the distribution is denser;
Marijuana: bamboo-like knots with gentle bulges and uneven distribution of knots;
Jute: no knots;
Apocynum: bamboo-like knots, more obvious, knotted The distribution is more even and the spacing is larger.
3. Texture
Ramie: longitudinal cracks or grooves, There are many “╳” shaped knife-like horizontal stripes;
Flax: Most fibers have a smooth surface, and some fibers have grooves or a few cracks and knives on the surface Chopped horizontal stripes;
Hemp: cylindrical fibers have a smooth surface with a few micropores, and flat fibers are partially rough, and some have vertical lines or grooves. groove.
Jute: with fine grooves or vertical lines
Apocynum: The surface of most fibers is extremely smooth, and some fibers have grooves on the surface
4. Head end shape
Ramie: sharp
Lax: sharp
Marijuana: Blunt Round
Apocynum: sharp
[ Cross-sectional morphology]
1. Geometric form
Ramie: oval or oblate, with cracks;
Line: round, oval or polygonal;
Marijuana: irregular triangle, quadrilateral, hexagon, oblate, waisted circle or polygon;
Jute: pentagonal or hexagonal;
Apocynum: round or oval.
2. Middle cavity
Ramie: oval or waist-round, with a smaller middle cavity Large;
Lax: The middle cavity is small ;
Marijuana: The middle cavity is larger, Oval in shape, accounting for about 1/2-1/3 of the cross-sectional area;
Jute: oval or round;
Apocynum: The middle cavity is smaller.
3. Others
The cross section of ramie fiber has radial cracks;
The length of ramie fiber is longer;
Due to the limited spinnability of the fiber itself, currently only ramie , linen and hemp have pure textiles;
The appearance and structure of the same variety of hemp fibers vary from different origins;
After production and processing, the hemp fibers are damaged and their appearance changes.
n style=”color: #343434; –tt-darkmode-color: #A3A3A3;”>4. Head end shape
Ramie: sharp
Lax: sharp
Marijuana: Blunt
Apocynum: sharp
[Cross-sectional shape]
1. Geometric form
Ramiie: oval or oblate, with Crack;
Lax: round, oval shape or polygon;
Marijuana: No Regular triangle, quadrilateral, hexagon, oblate circle, waist circle or polygon;
Jute: pentagonal or hexagonal;
Apocynum: round or oval.
2. Middle cavity
Ramie: oval or waist-round, with a smaller middle cavity Large;
Lax: The middle cavity is small ;
Marijuana: The middle cavity is larger, Oval in shape, accounting for about 1/2-1/3 of the cross-sectional area;
Jute: oval or round;
Apocynum: The middle cavity is smaller.
3. Others
The cross section of ramie fiber has radial cracks;
The length of ramie fiber is longer;
Due to the limited spinnability of the fiber itself, currently only ramie , linen and hemp have pure textiles;
The appearance and structure of the same variety of hemp fibers vary from different origins;
After production and processing, the hemp fibers are damaged and their appearance changes.







