Viscose
Viscose fiber is a regenerated cellulose fiber spun from natural cellulose (pulp) through cellulose xanthate solution.
The advent of viscose fiber is only later than cellulose nitrate fiber and is one of the oldest chemical fiber varieties. In 1891, Cross, Bevan and Beadle first prepared a solution of sodium cellulose xanthate. Because of the high viscosity of this solution, it was named “viscose”. After the viscose encounters acid, the cellulose precipitates again. Based on this principle, a method of preparing chemical fibers was developed in 1893. This fiber was named viscose fiber. By 1905, Muller and others invented a coagulation consisting of dilute sulfuric acid and sulfate, realizing the industrial production of viscose fiber.

Viscose Properties
|
Performance indicators |
Ordinary viscose short fiber |
Ordinary viscose filament |
High wet modulus viscose staple fiber |
|
|
Tensile strength/cN·dtex-1 |
Standard state |
2.2~2.7 |
1.5~2.0 |
3.4~4.6 |
|
Wet state |
1.2~1.8 |
0.7~ 1.1 |
2.5~3.7 |
|
|
Wet and dry strength ratio/% |
60~65 |
45~55 |
70~80 |
|
|
Elongation at break/% |
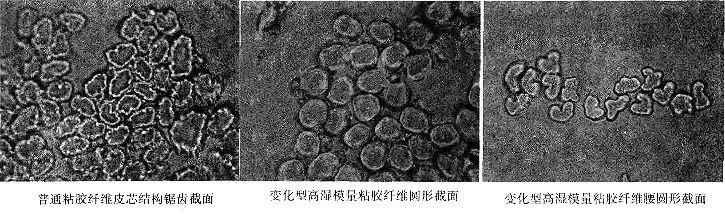
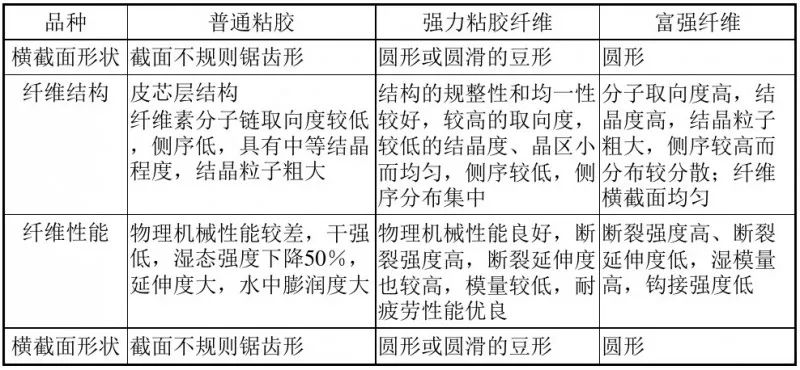
<p style="text-aliThe outer edge has an irregular zigzag shape, with an obvious skin-core structure; the structure has poor regularity and uniformity; the physical and mechanical properties are poor, with low dry strength, low wet strength, and large elongation; cellulose molecules The chain orientation is low, the side order is low, it has a medium degree of crystallization, and the crystalline particles are coarse.
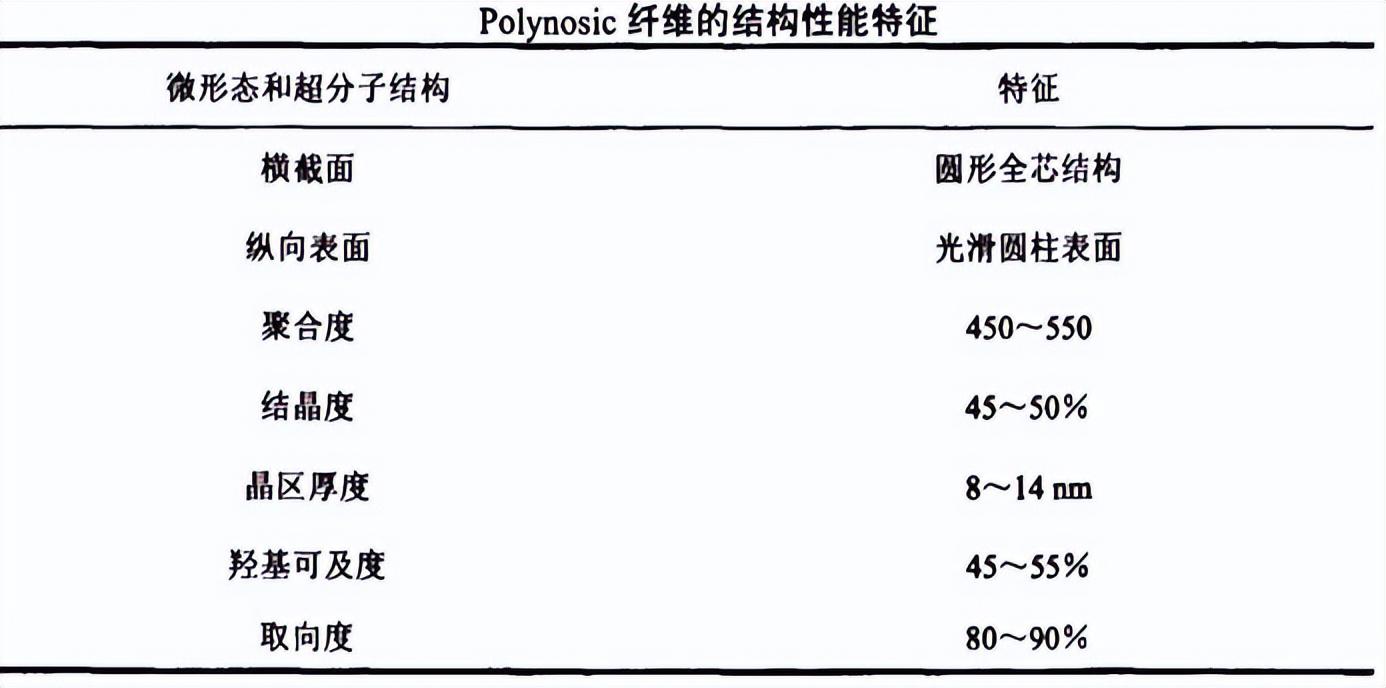
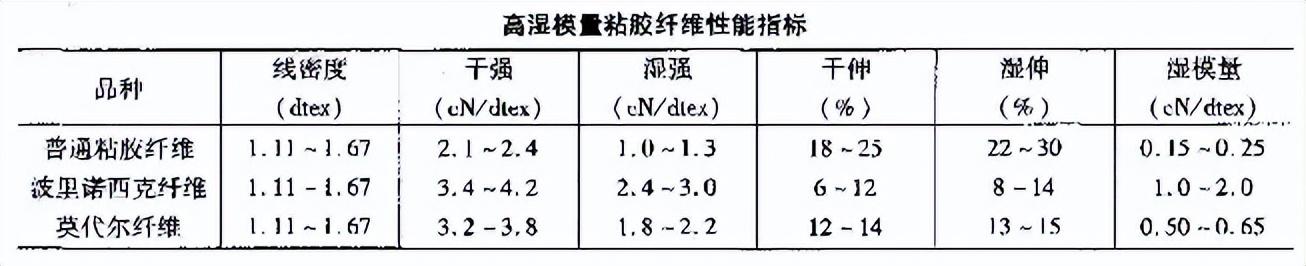
2 High wet modulus viscose fiber High wet modulus viscose fiber has high strength, wet modulus, and wet strength It is 22cN/tex, and the elongation does not exceed 15%. High wet modulus fibers can Divided into two categories: One type is Polynosic fiber, which was developed in Japan and is called tiger kapok in Japan. It was industrialized in the 1950s. The rich and strong fiber produced in my country in the 1960s is of the same type.
The other type is Variable high wet modulus fiberreferred to as high wet modulus fiber (HWM). The strength and wet modulus of this type of fiber are lower than Polynosic fiber, but the elongation at break is higher and the cohesion strength is particularly excellent, which basically overcomes the shortcomings of Polynosic fiber fibers with poor cohesion and high brittleness. The classic product is Modal fiber developed by the Austrian Lenzing company in the 1970s.
△Performance comparison 3 Strong viscose fiber Strong viscose fiber has high strength and fatigue resistance.
Cross-section structure: Strong adhesive: outside The margin is serrated and the cortex is thickened; Super Strong adhesive: denaturant, smooth surface, close to full-cortex structure; Second super and third super: the cross-section is close to a smooth circle, full-cortex structure, and the cross-sectional structure is relatively uniform. Fiber Properties The structure has good regularity and uniformity ; Higher orientation, lower The crystallinity and crystal area are small and uniform, the side order is low, and the side order distribution is concentrated; It has good mechanical properties, high breaking strength, high elongation at break, low modulus, and excellent fatigue resistance. 4 Modified viscose fiber Modified viscose fibers include grafted fibers, flame-retardant fibers, hollow fibers, conductive fibers, etc. Comparison of different types of viscose fibers
��Fibers include grafted fibers, flame-retardant fibers, hollow fibers, conductive fibers, etc. Comparison of different types of viscose fibers
This article is from the Internet, does not represent 【www.garmentmanufacture.com】 position, reproduced please specify the source.https://www.garmentmanufacture.com/archives/7259
| |||